- About Us
-
Research Report
Semiconductors
LED
Consumer Electronics
Emerging Technologies
- Selected Topics
- Membership
- Price Trends
- Press Center
- News
- Events
- AI Agent
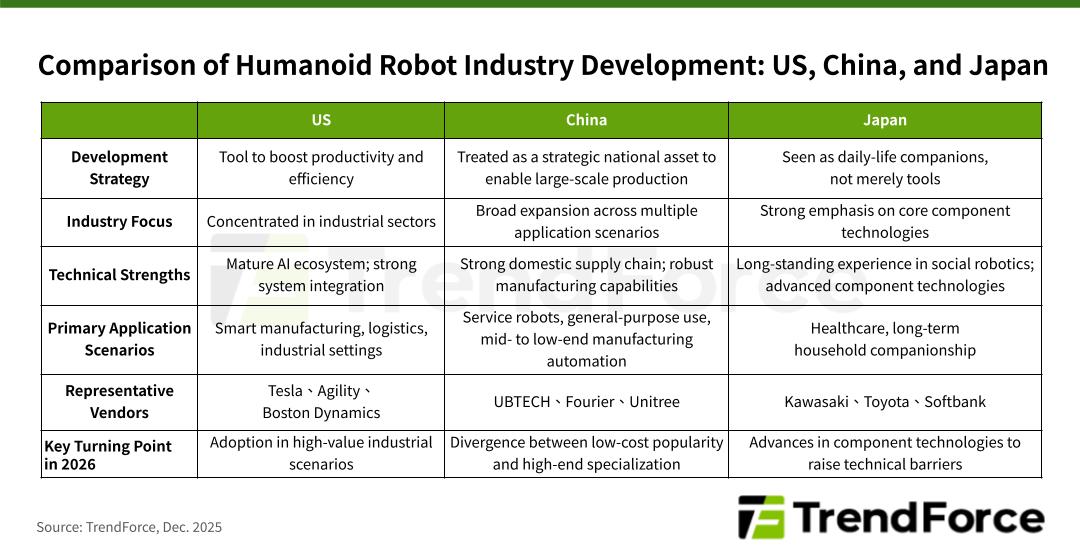
Major economies globally are advancing humanoid robot development. Japan is focusing on improving essential components like actuators, sensors, and control systems to increase the entry barrier. In contrast, the U.S. and China are rapidly rolling out end-to-end humanoid products. Since these regions focus on different application scenarios, their humanoid robot industries are likely to reach key turning points in 2026.
TrendForce forecasts 2026 as a pivotal year for the commercialization of humanoid robots, with global shipments expected to exceed 50,000 units, marking over 700% YoY growth.
At the recent iREX 2025 exhibition in Tokyo, Kawasaki Heavy Industries revealed its newest humanoid, Kaleido 9. This robot can lift loads of 30 kg, learn to operate cleaning tools, and support remote control through VR headsets, making it suitable for disaster response. Harmonic Drive also presented optimized reducer designs specifically for humanoid joints: flat, high-torque reducers for the neck and arms, and ultra-compact models for fingers to improve grasping capabilities.
Although humanoids were the main focus of iREX 2025, TrendForce’s on-site observations showed that industrial robotic arms and cobots were the most prominent exhibits. This highlights Japan’s ongoing emphasis on mature industrial applications, where integration, deployment, and ROI are well understood, despite Japan’s strong expertise in humanoid-related technologies like integrated sensing, precision joints, and advanced control systems.
However, Japan’s widening elder-care labor gap—and its dense network of care facilities—has made reducing caregiver burden and improving care quality an urgent priority. Consequently, TrendForce expects eldercare to become Japan’s strongest and fastest-growing humanoid application scenario. Kawaski’s Nyokkey and Fourier’s GR-3 are both designed with this use case in mind.
In contrast, the U.S. humanoid industry has moved from showcasing technology demos to focusing on real-world testing. The key to competitive advantage now lies in system integration and deploying scenarios, rather than merely movement ability. Companies like Tesla, Boston Dynamics, and Agility Robotics are prioritizing long-lasting operational stability, energy efficiency, and real-time AI inference on devices.
TrendForce predicts 2026 to be a watershed year for entry, where U.S. vendors will determine if they can develop scalable business models in manufacturing logistics and, ultimately, in consumer services, paving the way from R&D to widespread deployment.
China’s humanoid robotics industry features a variety of application scenarios and tiered pricing models. Unitree and Agibot are focused on large-scale pilot programs using affordable models to build a consumer base, whereas Fourier emphasizes rehabilitation and companionship through emotional interaction and medical knowledge. Meanwhile, UBTECH, supported by significant funding, is rapidly expanding the use of humanoid robots in automotive manufacturing.
TrendForce observes that China’s main challenge in 2026 will be maintaining a balance between making products affordable for the mass market and offering high-end differentiation, while also developing sustainable data and application ecosystems.
For more information on robot reports and market data from TrendForce, please visit https://www.trendforce.com.tw/research/category/Emerging%20Technologies/robot or contact SR_MI@trendforce.com for a free sample of the 2025 market outlook.
Subject
Related Articles
Related Reports

